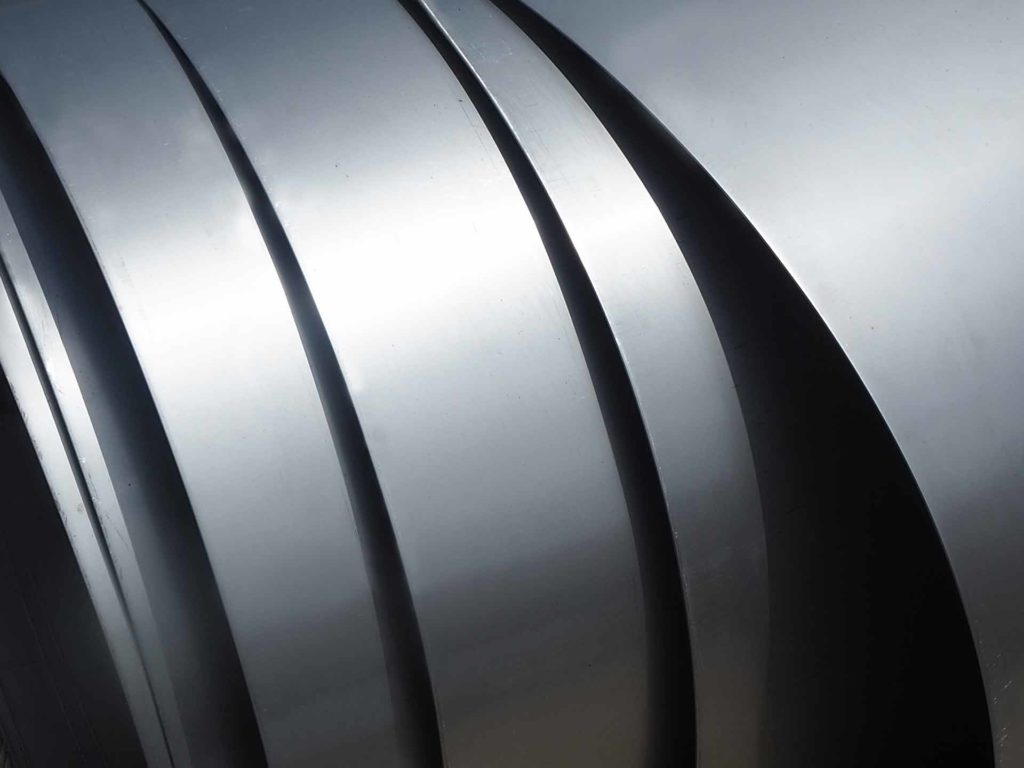
Stainless Steel Sheet & Plate
- Home
- >
- Stainless Steel
- >
- Sheet & Plate

Selective Sheets & Plates

2B

No.1
Available Specification
| Stainless Steel Sheet/Plate Information | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Surface Finish | Grade Series | Thickness(mm) | Width(mm) | Application | |||||
| Main Dimension | ||||||||||
| 20-850 | 1000 | 1219 | 1240 | 1250 | 1500 | |||||
| Hot Rolled | No.1 /2D | 201/304 | 2.2-12.0 | Petro-chemical industry Tanks Construction material | ||||||
| Cold Rolled | 2B | 201/304 | 0.25-3.0 | |||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| No.4 / Hairline Mirror / Linen SB | 201/304 | 0.22-3.0 | ||||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| BA | 201/304 | 0.2-1.8 | ||||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| 2BA | ||||||||||
| Chemical composition and mechanical properties of stainless steel sheet/plate | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Chemical Composition (%) | Mechanieal Performece | |||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | Hardness | |||
| 201 | ≤0.15 | ≤1.00 | 5.5/7.5 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.030 | 3.5/5.5 | 16.0/18.0 | - | HB≤241,HRB≤100, HV≤240 | ||
| 304 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.03 | 8.0/11.0 | 18.00/20.00 | - | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 316 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.03 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.0/18.0 | 2.00/3.00 | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 316L | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.03 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.0/18.0 | 2.00/3.00 | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 410 | ≤0.15 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.25 | ≤0.060 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.060 | 11.5/13.5 | - | HB≤183, HRB≤88,HV≤200 | ||
| 430 | ≤0.12 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.25 | ≤0.040 | ≤0.03 | - | 16.00/18.00 | - | HB≤183, HRB≤88,HV≤200 | ||
Significant Advantage
Better Strength
Comprehensive Uses
Typical Applications
Food Processing
Storage Tanks
Construction
Kitchen Equipment

Brushed
Polished
Etched
Embossed
Anti-Fingerprint
Colored

Bead Blasting
Perforated
Water Ripple

Ready to Start Your Customization Project?
Stainless Steel Sheet&Plate Manufacturing Process
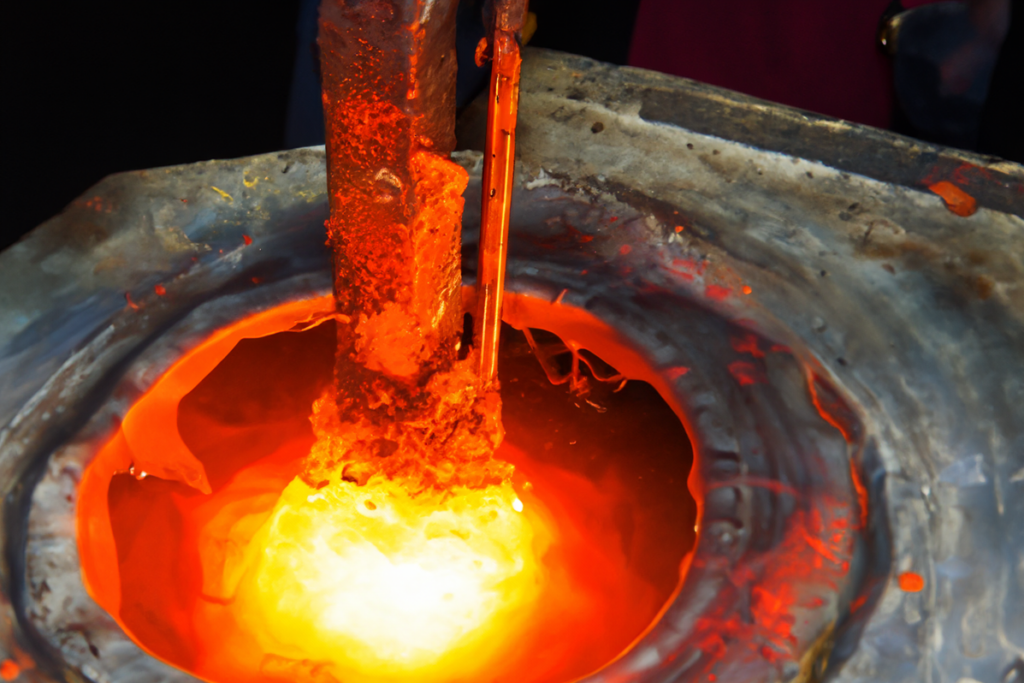

Melting
Melting the raw materials including iron ore, nickel, chromium, and other alloys in a furnace to create molten metal at high temperatures.
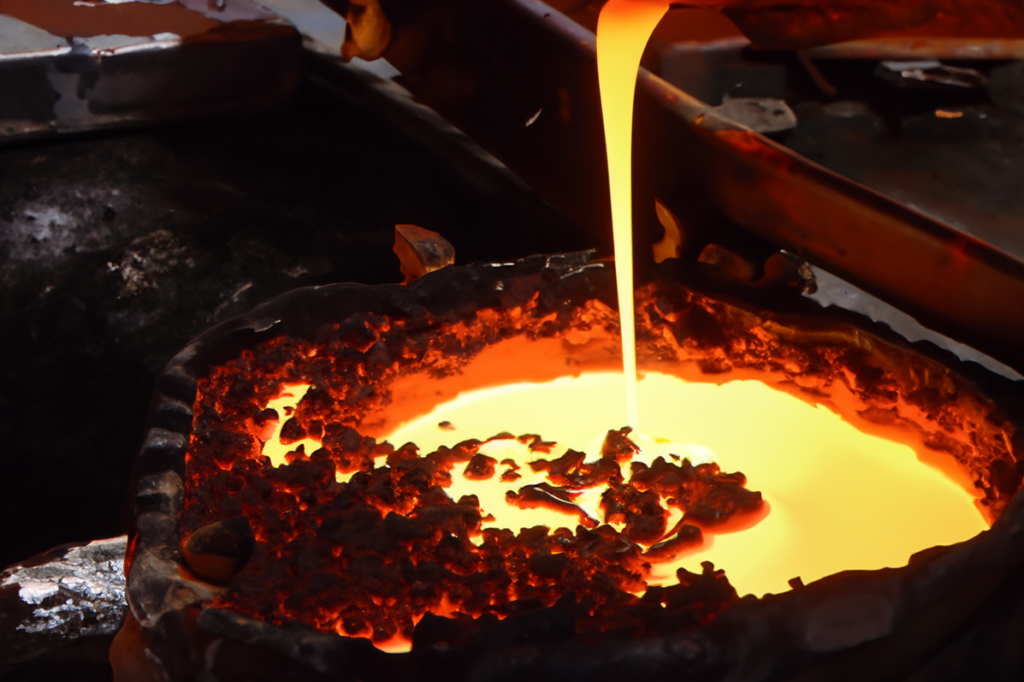

Casting
Molten metal poured into a mold to create large slabs or billets of stainless steel.
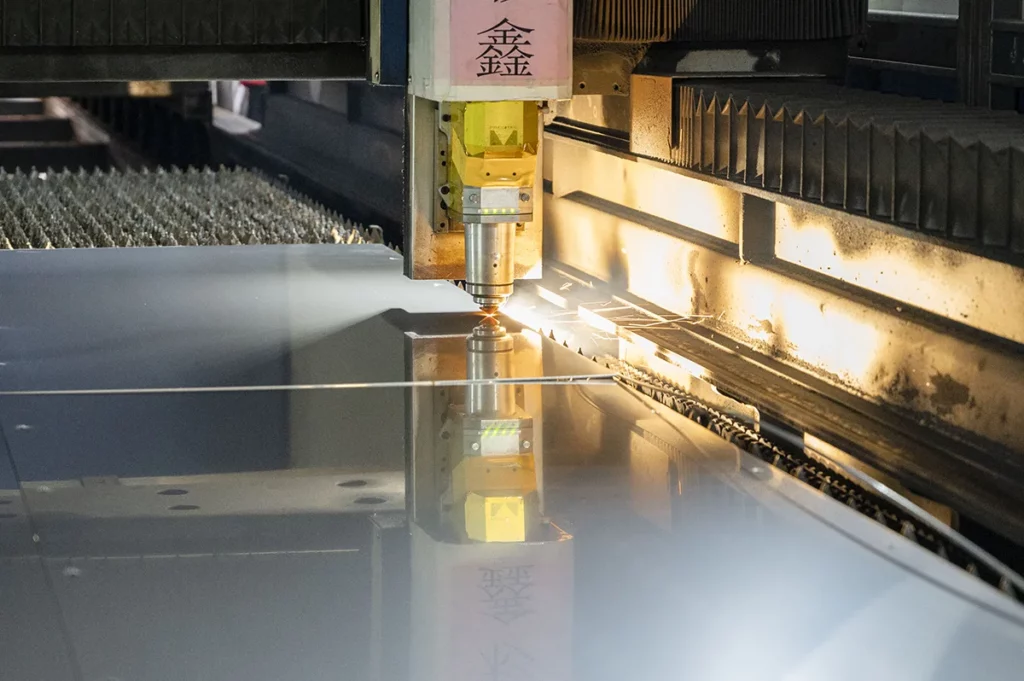

Rolling
Slab heated and rolled several times into thinner sheets or plates using a series of rolling mills.

Annealing
Stainless steel sheets or plates are annealed to remove any stresses and improve their ductility and toughness.
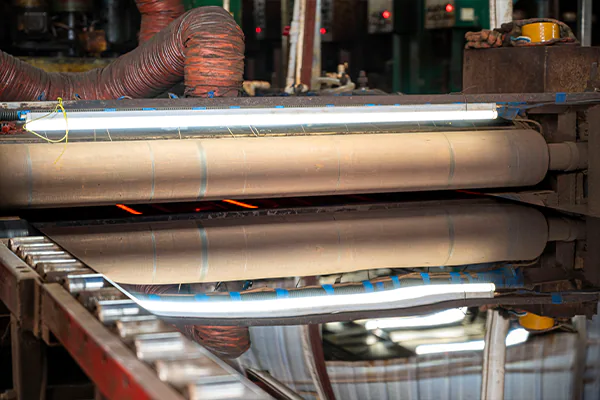

Finishing
Polishing, grinding, or coating the plates or shheets’ surface to improve its appearance and protect it from corrosion.
Stainless Steel Sheet vs. Stainless Steel Plate
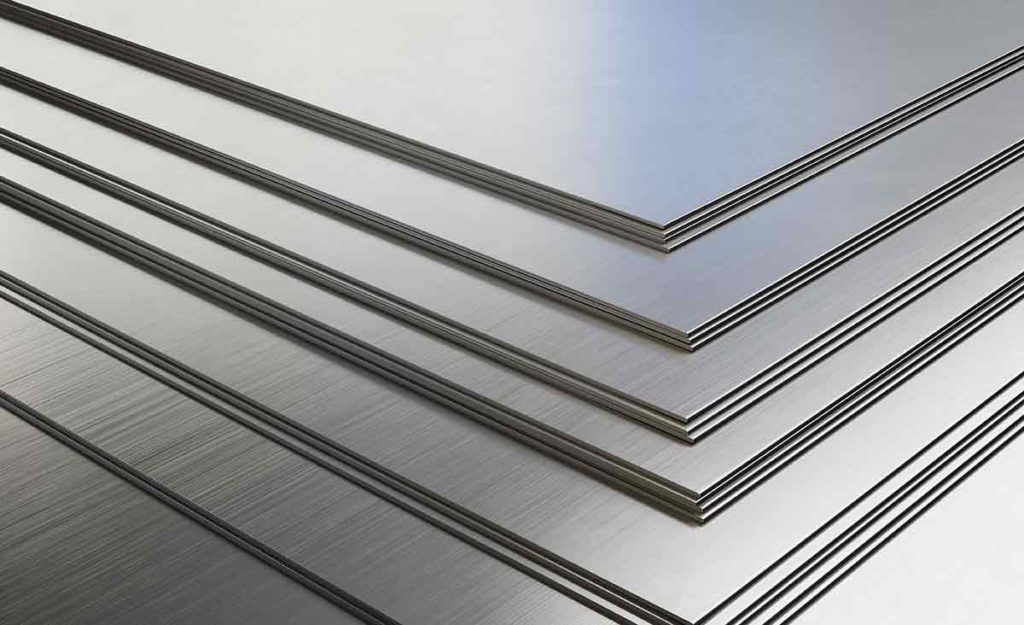

| Feature | Stainless Steel Sheets | Stainless Steel Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.4mm-6mm | Typically 6mm-100mm |
| Size | Come in a variety of sizes | Typically larger sizes |
| Use | Decorative purposes, such as in kitchen appliances, back splashes, and wall coverings | Industrial applications, such as in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries |
| Cutting | Sold in standard sizes | Often cut to size from larger sheets |
Applications of Common Grades
| Grade | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | Excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, good formability | Food processing, chemical processing, medical equipment |
| 316 | Excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments | Marine applications, chemical processing, medical equipment |
| 430 | Magnetic, good corrosion resistance | Automotive trim, appliances |
| 410 | Cutlery, surgical instruments, turbine blades | Often cut to size from larger sheets |
Applications of Stainless Steel Sheets & Plates
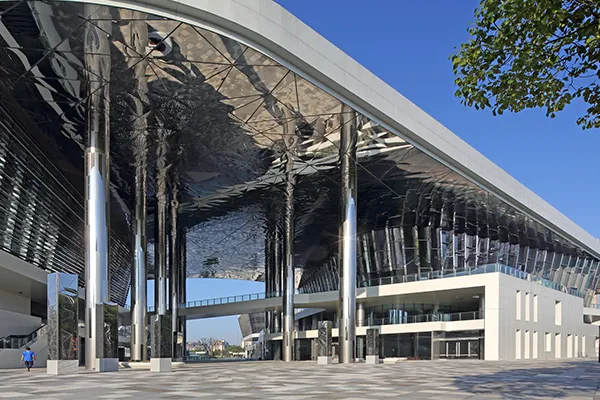

Construction
Stainless steel plates and sheets are commonly used in the construction industry due to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They are used for making structural members, roofing, cladding, and reinforcement bars
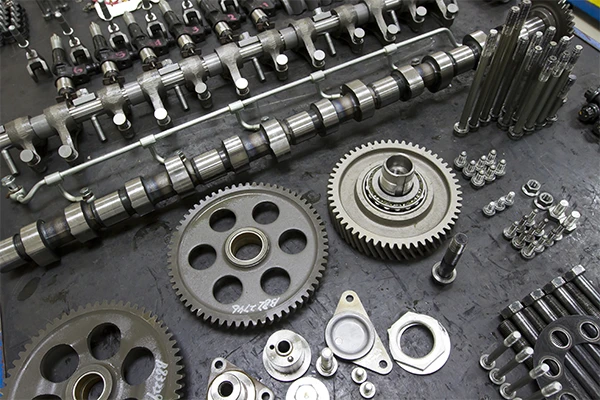

Automotive Industry
Stainless steel is used extensively in the automotive industry due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. It is used for making exhaust systems, mufflers, trim, and other components.
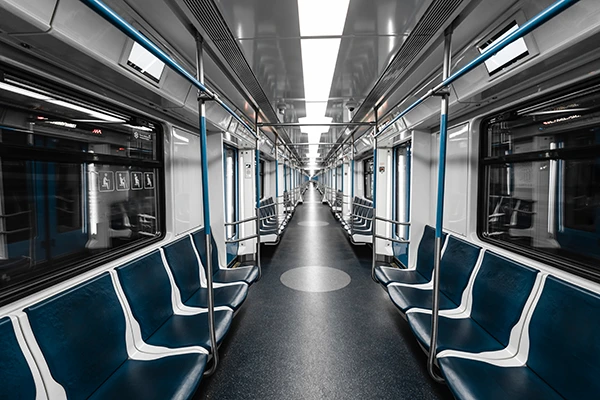

Transport Industry
Stainless steel is used in the transport industry due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance requirements. It is used for manufacturing components such as subway carriages, aircraft parts, shipbuilding, and railway infrastructure.
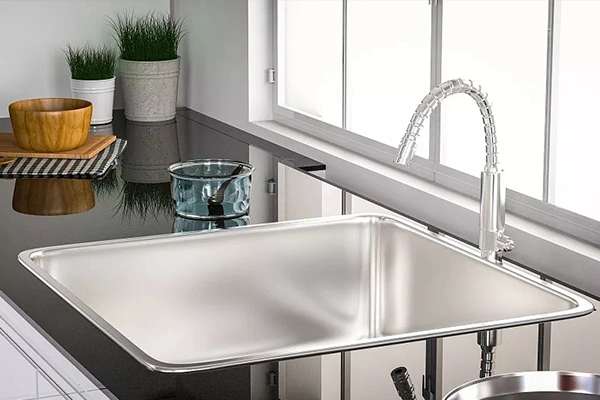

Kitchen Equipment
Stainless steel is widely used in kitchen equipment due to its hygiene, durability, and ease of cleaning, making it suitable for making appliances such as sinks, cookware, and refrigerators.
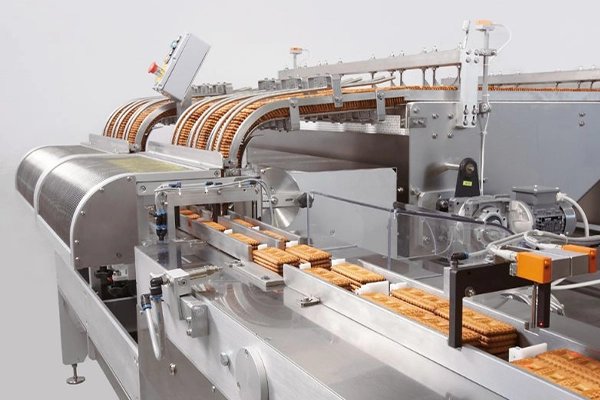

Food Processing Industry
Stainless steel is used for making equipment such as storage tanks, mixing tanks, and processing machinery due to corrosion resistance, hygiene, and ease of cleaning.
Medical Industry
Stainless steel is used in medical devices and equipment due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength. It is used for making surgical instruments, implants, and orthodontic appliances.
Quality Control
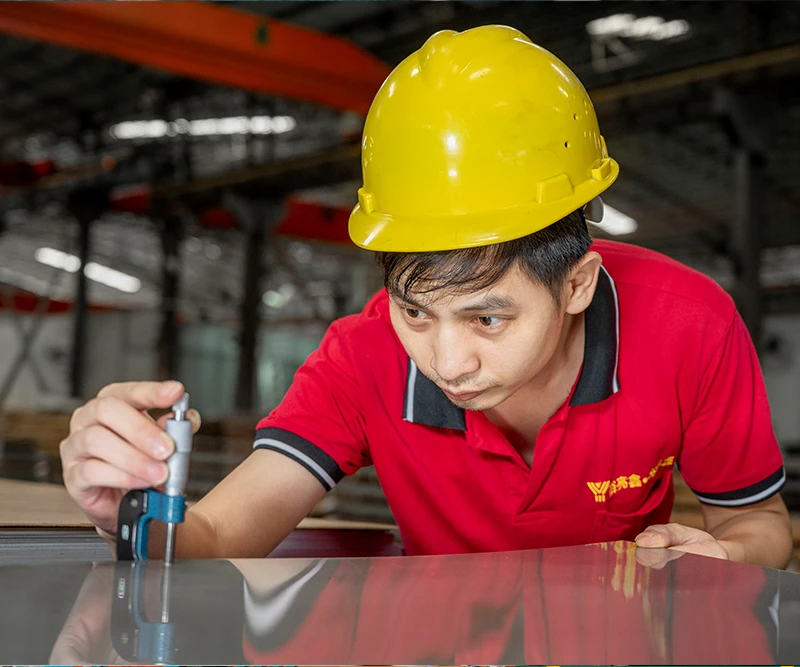

1. Raw Material Inspection
Inspect the chemical composition, physical properties, and dimensions of the raw materials used in the manufacturing process.
2. In-process Inspection
During the manufacturing process, check the thickness, width, and length of the stainless steel sheets or plates, and conduct tests to ensure that the material is free from defects.
3. Final Inspection
Conduct a final inspection to to check the surface finish, dimensions, and mechanical properties of the stainless steel sheets or plates.
4. Testing
Conduct various tests to ensure that the product meets the required quality standards. This includes tests for corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and hardness.
5. Documentation
Document all inspection and testing results to ensure that the product meets the required quality standards and can be traced back to the manufacturing process.
How to Choose the Right Thickness?
1. Determine the Load and Stress
The first step is to determine the load and stress that the plate will be subjected to. This includes considering factors such as the weight of the load, the frequency of use, and any impact or vibration that may occur.
5. Consult Plate Thickness Charts
Consult plate thickness charts that are available from experts or stainless steel plate suppliers to determine the recommended thickness for the chosen material based on the load and stress.
2. Consider the Plate's Structural Role
6. Add a Safety Factor
To ensure that the plate can withstand unexpected or extreme loads, it is recommended to add a safety factor when choosing the plate thickness. A typical safety factor is 1.5 to 2 times the calculated thickness.
3. Determine the Required Strength
Based on the load, stress, and structural role, determine the required strength that the plate must have. This includes considering the yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation properties of the stainless steel.
7. Consider Corrosion Resistance
Finally, consider the corrosion resistance of the chosen plate material and how it may be affected by the application environment. This includes considering the potential for exposure to chemicals, saltwater, or extreme temperatures.
4. Identify the Plate Material
Based on the required strength properties, identify the appropriate stainless steel material that is suitable for the application.