Tôle d'acier inoxydable & Plaque
- Maison
- >
- Acier inoxydable
- >
- Feuille & Plaque

Feuilles sélectives & Assiettes

2B

N°1
Spécification disponible
| Informations sur les tôles/plaques d'acier inoxydable | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Finition de surface | Série de qualité | Épaisseur(millimètre) | Largeur(millimètre) | Application | |||||
| Dimension principale | ||||||||||
| 20-850 | 1000 | 1219 | 1240 | 1250 | 1500 | |||||
| Laminé à chaud | N°1 /2D | 201/304 | 2.2-12.0 | Industrie pétrochimique Citernes Matériaux de construction | ||||||
| Laminé à froid | 2B | 201/304 | 0.25-3.0 | |||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| Numéro 4 / Miroir délié / Lin SB | 201/304 | 0.22-3.0 | ||||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| BA | 201/304 | 0.2-1.8 | ||||||||
| 410S/430 | 0.25-2.0 | |||||||||
| 2BA | ||||||||||
| Composition chimique et propriétés mécaniques des tôles/plaques d'acier inoxydable | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noter | Composition chimique (%) | Performance mécanique | |||||||||
| C | Et | Mn | P | S | Dans | Cr | mois | Dureté | |||
| 201 | ≤0.15 | ≤1.00 | 5.5/7.5 | ≤0,060 | ≤0,030 | 3.5/5.5 | 16.0/18.0 | - | HB≤241,HRB≤100, HV≤240 | ||
| 304 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0,045 | ≤0.03 | 8.0/11.0 | 18.00/20.00 | - | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 316 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0,045 | ≤0.03 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.0/18.0 | 2.00/3.00 | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 316L | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.0 | ≤0,045 | ≤0.03 | 10.00/14.00 | 16.0/18.0 | 2.00/3.00 | HB≤187, HRB≤90,HV≤200 | ||
| 410 | ≤0.15 | ≤1.00 | ≤1,25 | ≤0,060 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,060 | 11.5/13.5 | - | HB≤183, HRB≤88,HV≤200 | ||
| 430 | ≤0.12 | ≤1.00 | ≤1,25 | ≤0,040 | ≤0.03 | - | 16.00/18.00 | - | HB≤183, HRB≤88,HV≤200 | ||
Avantage significatif
Meilleure force
Utilisations complètes
Applications typiques
Préparation des aliments
Réservoirs de stockage
Construction
Équipement de cuisine

Brossé
Brillant
Gravée
En relief
Anti-empreintes digitales
Coloré

Grenaillage de perles
Perforé
Ondulation de l'eau

Prêt à démarrer votre projet de personnalisation?
Tôle d'acier inoxydable&Processus de fabrication des plaques
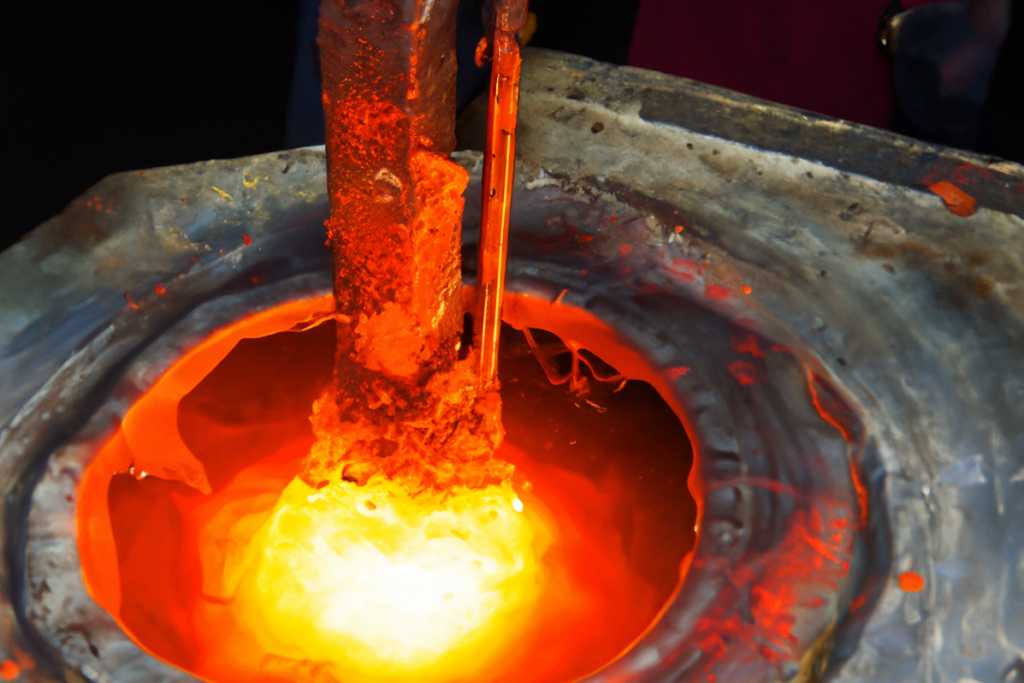

Fusion
Faire fondre les matières premières dont le minerai de fer, nickel, chrome, et d'autres alliages dans un four pour créer du métal en fusion à haute température.
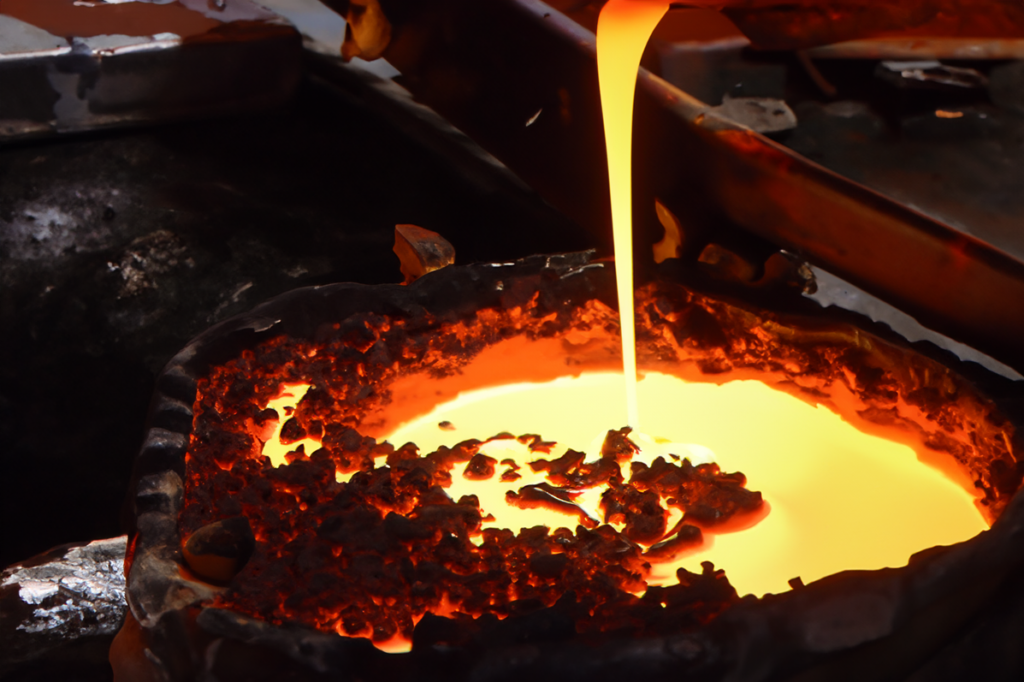

Fonderie
Métal en fusion versé dans un moule pour créer de grandes dalles ou billettes d'acier inoxydable.
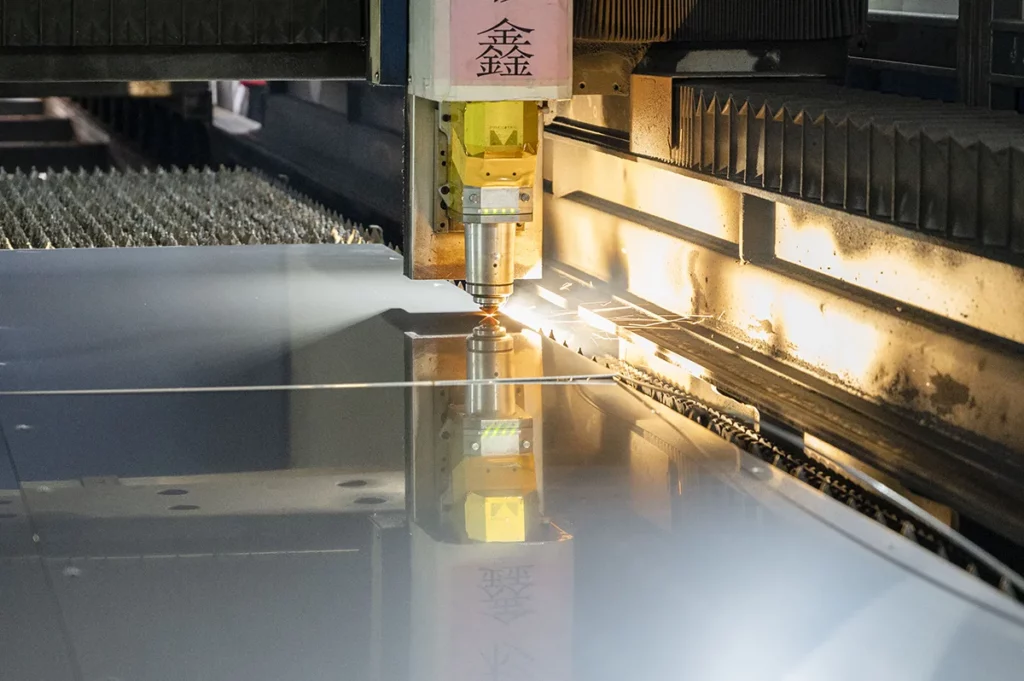

Roulant
Dalle chauffée et laminée plusieurs fois en feuilles ou plaques plus minces à l'aide d'une série de laminoirs.

Recuit
Les tôles ou plaques d'acier inoxydable sont recuites pour éliminer toutes contraintes et améliorer leur ductilité et leur ténacité..
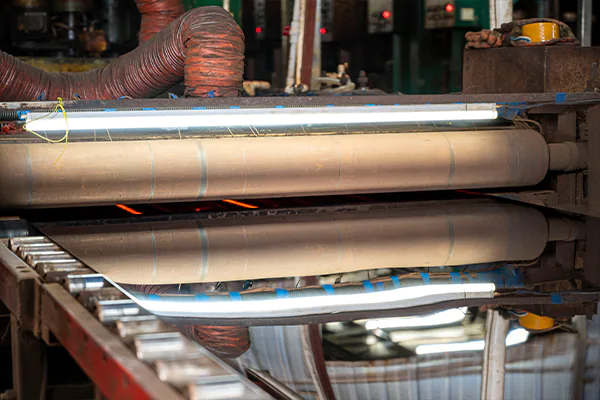

Finition
Polissage, affûtage, ou enduire les plaques ou feuilles’ surface pour améliorer son aspect et la protéger de la corrosion.
Tôle d'acier inoxydable vs. Plaque en acier inoxydable

| Fonctionnalité | Tôles d'acier inoxydable | Plaques en acier inoxydable |
|---|---|---|
| Épaisseur | Généralement 0,4 mm-6 mm | Généralement 6 mm-100 mm |
| Taille | Venez dans une variété de tailles | Tailles généralement plus grandes |
| Utiliser | Fins décoratives, comme dans les appareils de cuisine, dosserets, et revêtements muraux | Applications industrielles, comme dans la construction, automobile, et industries aérospatiales |
| Coupe | Vendu en tailles standards | Souvent découpé à partir de feuilles plus grandes |
Applications des qualités communes
| Noter | Propriétés | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | Excellente résistance à la corrosion, résistance à haute température, bonne formabilité | Préparation des aliments, traitement chimique, équipement médical |
| 316 | Excellente résistance à la corrosion, en particulier dans les environnements difficiles | Applications marines, traitement chimique, équipement médical |
| 430 | Magnétique, bonne résistance à la corrosion | Garniture automobile, appareils électroménagers |
| 410 | Coutellerie, Instruments chirurgicaux, des aubes de turbine | Souvent découpé à partir de feuilles plus grandes |
Applications des tôles d'acier inoxydable & Assiettes
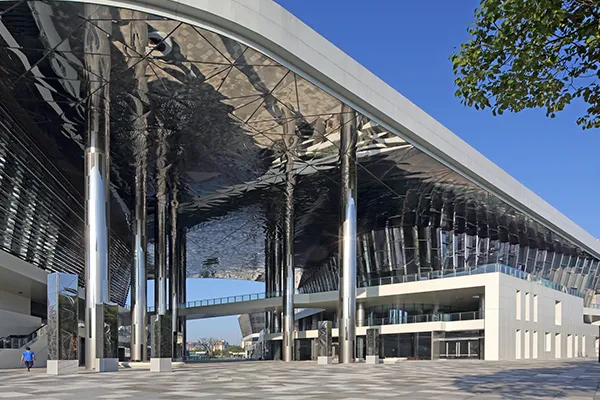

Construction
Les plaques et tôles en acier inoxydable sont couramment utilisées dans l'industrie de la construction en raison de leur durabilité., force, et résistance à la corrosion. Ils sont utilisés pour fabriquer des éléments de structure, toiture, bardage, et barres de renfort
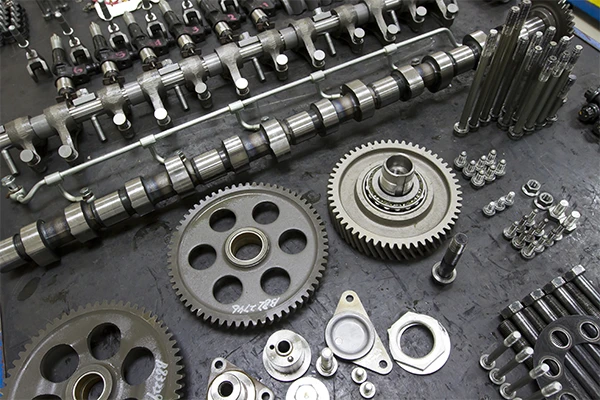

Industrie automobile
L'acier inoxydable est largement utilisé dans l'industrie automobile en raison de sa résistance., résistance à la corrosion, et attrait esthétique. Il est utilisé pour fabriquer des systèmes d'échappement, silencieux, garniture, et d'autres composants.
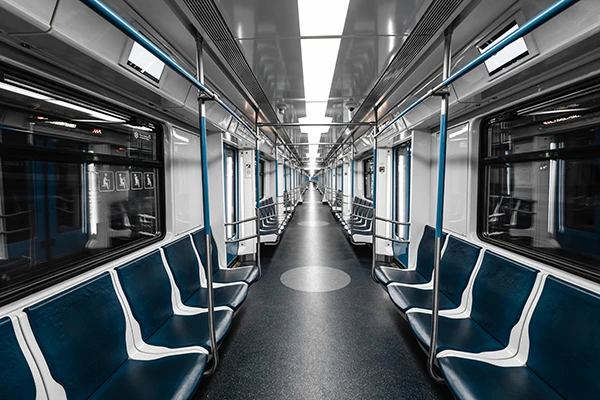

Industrie des transports
L'acier inoxydable est utilisé dans l'industrie du transport en raison de sa haute résistance, résistance à la corrosion, et faibles besoins d'entretien. Il est utilisé pour fabriquer des composants tels que des rames de métro, pièces d'avion, construction navale, et infrastructures ferroviaires.
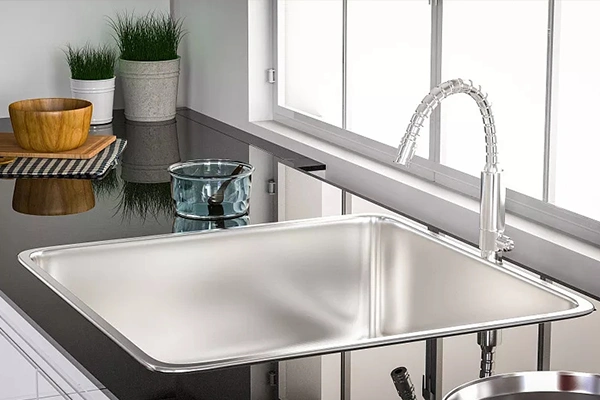

Équipement de cuisine
L'acier inoxydable est largement utilisé dans les équipements de cuisine en raison de son hygiène, durabilité, et facilité de nettoyage, ce qui le rend adapté à la fabrication d'appareils tels que des éviers, batterie de cuisine, et réfrigérateurs.
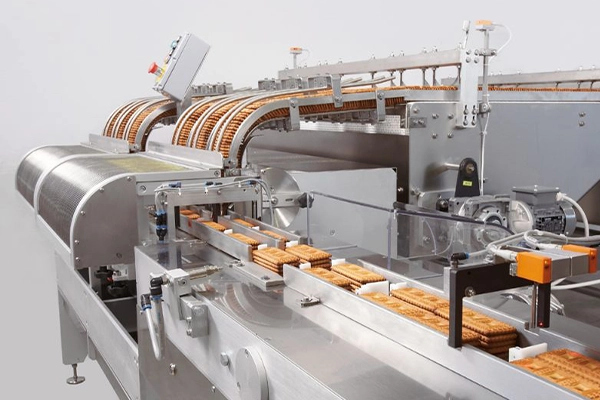

Industrie de transformation des aliments
L'acier inoxydable est utilisé pour fabriquer des équipements tels que des réservoirs de stockage, cuves de mélange, et machines de traitement en raison de la résistance à la corrosion, hygiène, et facilité de nettoyage.
Industrie médicale
L'acier inoxydable est utilisé dans les dispositifs et équipements médicaux en raison de sa biocompatibilité, résistance à la corrosion, et la force. Il est utilisé pour fabriquer des instruments chirurgicaux, implants, et appareils orthodontiques.
Contrôle de qualité
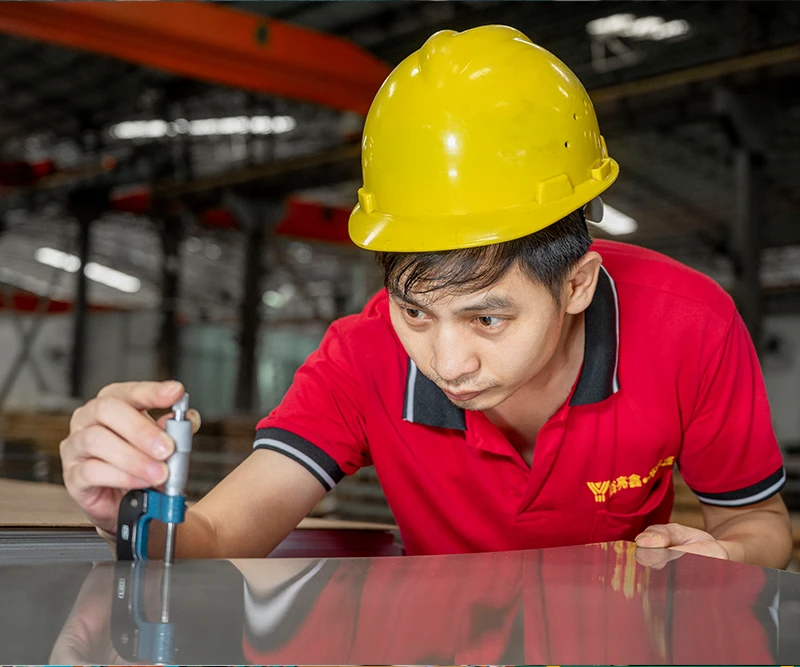

1. Inspection des matières premières
Inspecter la composition chimique, propriétés physiques, et dimensions des matières premières utilisées dans le processus de fabrication.
2. En cours d'inspection
Pendant le processus de fabrication, vérifier l'épaisseur, largeur, et longueur des tôles ou plaques d'acier inoxydable, et effectuer des tests pour garantir que le matériau est exempt de défauts.
3. L'inspection finale
Effectuer une inspection finale pour vérifier la finition de la surface, dimensions, et propriétés mécaniques des tôles ou plaques d'acier inoxydable.
4. Essai
Effectuer divers tests pour s'assurer que le produit répond aux normes de qualité requises. Cela comprend des tests de résistance à la corrosion, résistance à la traction, et dureté.
5. Documentation
Documenter tous les résultats d'inspection et de test pour garantir que le produit répond aux normes de qualité requises et peut être retracé jusqu'au processus de fabrication..
Comment choisir la bonne épaisseur?
1. Déterminer la charge et la contrainte
La première étape consiste à déterminer la charge et la contrainte auxquelles la plaque sera soumise.. Cela inclut la prise en compte de facteurs tels que le poids de la charge, la fréquence d'utilisation, et tout impact ou vibration pouvant survenir.
5. Consultez les tableaux d’épaisseur des plaques
Consultez les tableaux d'épaisseur de plaque disponibles auprès d'experts ou sfournisseurs de tôles d'acier inoxydable pour déterminer l'épaisseur recommandée pour le matériau choisi en fonction de la charge et des contraintes.
2. Considérez le rôle structurel de la plaque
6. Ajouter un facteur de sécurité
Pour garantir que la plaque peut résister à des charges inattendues ou extrêmes, il est recommandé d'ajouter un facteur de sécurité lors du choix de l'épaisseur de la plaque. Un facteur de sécurité typique est 1.5 pour 2 multiplié par l'épaisseur calculée.
3. Déterminer la force requise
Basé sur la charge, stresser, et rôle structurel, déterminer la résistance requise que la plaque doit avoir. Cela inclut la prise en compte de la limite d'élasticité, résistance à la traction, et propriétés d'allongement de l'acier inoxydable.
7. Pensez à la résistance à la corrosion
Enfin, prendre en compte la résistance à la corrosion du matériau de plaque choisi et la façon dont il peut être affecté par l'environnement d'application. Cela inclut la prise en compte du potentiel d'exposition à des produits chimiques, eau salée, ou des températures extrêmes.
4. Identifiez le matériau de la plaque
Basé sur les propriétés de résistance requises, identifier le matériau en acier inoxydable approprié qui convient à l'application.